
How much do you see HKUST publications in social media? Using Altmetric Explorer, we find that attention to our research has risen sharply in 2021. Can you guess who was talking about our works, and where?
Social Attention: Counting "Mentions"
Before we show you the data, you would first need to know how to measure "attention" in social media. A traditional way to measure academic influence is counting how many times a paper or a book is cited. To measure research impact beyond academic discourse, people started to use new ways of counting, called altmetrics. For example, we capture the number of tweets or blog posts that mention a particular research work to evaluate the attention it gets in social media. Specifically, to see research impact on society and technological applications, we are also interested to track citations in policy documents and patents. In the database Altmetric Explorer, these counts are called "mentions".
"Mentions" of HKUST Research
In a search conducted on Feb 24, 2022, Altmetric Explorer found almost 105,000 mentions of about 15,000 HKUST research outputs. These mentions appeared in various sources:
| Source | Number of Mentions |
|---|---|
| News | 5515 |
| Blog | 1197 |
| Policy | 589 |
| Patent | 12054 |
| 82242 | |
| Peer review | 144 |
| 42 | |
| 1372 | |
| Wikipedia | 1015 |
| Google+ | 324 |
| 0 | |
| 154 | |
| 0 | |
| F1000 | 146 |
| Q&A | 30 |
| Video | 104 |
Over the years, the number of mentions of HKUST research publications have been rising (Figure 1). It doubled from 8,000 in 2019 to over 16,000 in 2020; then jumped to over 41,000 in 2021. You can see that the increase was largely driven by the blue portion, which is... Twitter!
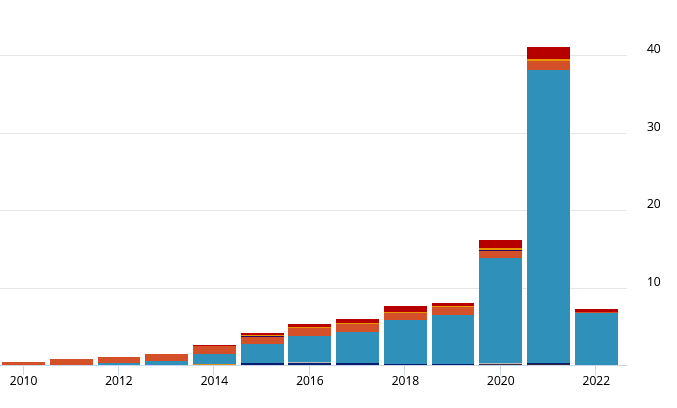
Figure 1 (data as of Feb 24, 2022)
The Tweets and the Tweeters
Below are the top tweeted HKUST-affiliated papers; follow the links to see their almetrics data:
- An evidence review of face masks against COVID-19
- Aerodynamic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 in two Wuhan hospitals
- Pan-cancer analysis of whole genomes
- Frankly, We Do Give a Damn
- Combined Measurement of the Higgs Boson Mass in pp Collisions at √s=7 and 8 TeV with the ATLAS and CMS Experiments
As you would expect, many Twitter accounts that are interested in our research are academic, such as BlackPhysicist, UCL Discovery, BioRxiv, and Journal of Management.
Coverage in News Media
News sources also mention our research. They may be research-oriented news outlets such as Phys.org, AAAS's EurekaAlert, and Science Daily. There are academic journalism sites such as The Conversation. Mainstream newspapers also cover stories that cite research work, including New York Times, Vice, BBC News, and many others. For example, an article with two authors from our Department of Marketing, "The “Self” under COVID-19: Social role disruptions, self-authenticity and present-focused coping," was quoted in a recent article in The Guardian (2022 Jan 4):
Figure 2
In the screenshot (Figure 3), you can see the top papers that have received the most news outlets coverage in our search. It is not surprising that many are Covid-related research:
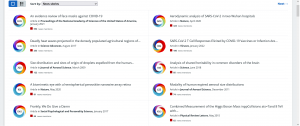
Figure 3
Attention of Policy Makers and International Agencies
While research publications may catch attention of news media soon after they are published, it often takes long time for research works to get cited in policy documents such as analysis or consultancy reports. However, these appearances can be good indicators of how research leads to social impact. In our search in Altmetric Explorer, we can find out which papers are quoted in policy documents (Figure 4):
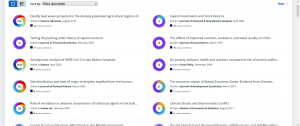
Figure 4
For example, a 2008 paper "Do poverty and poor health and nutrition increase the risk of armed conflict onset?" was cited multiple times by UNICEF, FAO United Nations, World Bank and the UK Government (Figure 5):
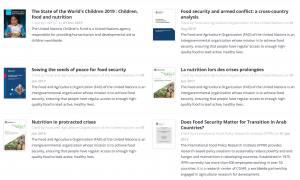
Figure 5
About Altmetric Explorer
While altmetrics is the generic term for new ways to measure research impact, Altmetric Explorer is a proprietary database. As shown in this post, you can use it to find "mentions" of research publications, either searching with the affiliated institutions, authors (using ORCID iDs), or specific published works (using PIDs such as doi). The Library has subscription to this database for the current year. Take the opportunity to try it out!






