
Using the Topic Modeling Tool developed under the Library’s DS CoLab project, we applied a natural language processing (NLP) approach to analyze posts from the HKUST Library’s Research Bridge Blog.
In the digital age, understanding thematic trends in academic context is essential for libraries and research institutions to better align their resources with user needs. Our goal was to uncover underlying themes, track their evolution over time, and explore their potential relationship with reader engagement.
Methodology
Data & Tools
We analyzed blog post data (as of June 17, 2025), combining the “Title” and “Content” fields after removing HTML tags. Using our in-house Topic Modeling Tool, we:
- Set the minimum number of topics to 10 but allowed the algorithm to optimize for coherence, resulting in 5 robust topics.
- Treated “research” as a stop word to reduce noise, as it appeared frequently across all topics.
- Visualized our results with 2D cluster plots, word clouds, and topic trend graphs.
Key Steps
- Topic Identification: Extracted top keywords per topic and validated them against manually assigned blog tags and categories.
- Temporal Analysis: Tracked topic frequency using publication dates to observe changes over time.
Findings & Insights
Topic Breakdown & Keywords
Despite the small dataset (around 200 posts from 2018 to mid-2025), the model identified five distinct and coherent topics. Removing the word “research” significantly improved topic separation. Below is a snapshot of the topics:
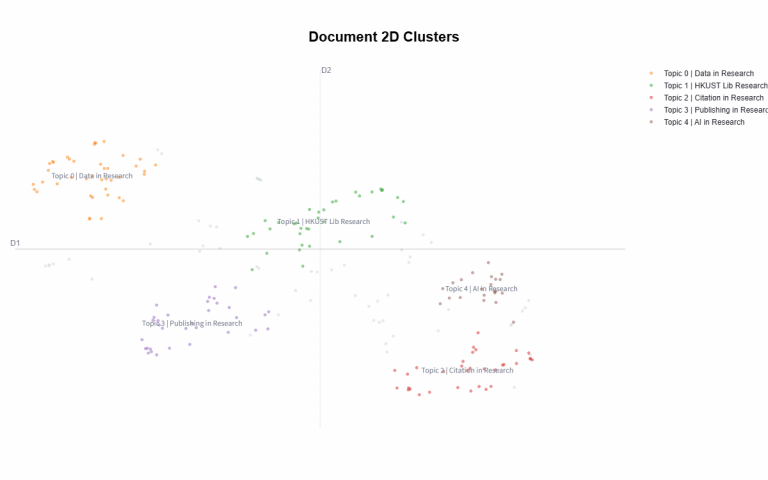
1. Data in Research
- Keywords: data , sharing, dataset, management, DMP
- Context: This topic dominates discussions on data stewardship, emphasizing practical aspects like dataset sharing, Data Management Plans (DMPs), and institutional resources (e.g., HKUST).
2. HKUST Lib Research
- Keywords: library, availability, new, ORCID, social
- Context: Focuses on library services and updates, including resource availability (e.g., new databases) and researcher profiles (ORCID).
3. Citation in Research
- Keywords: citation, papers, impact, Altmetric, Scite
- Context: Centers on citation metrics, academic impact, and tools (e.g., Altmetric, Scite).
4. Publishing in Research
- Keywords: OA, open, access, publishing, authors
- Context: Dominated by open access (OA) publishing, journal agreements, and author guidelines.
5. AI in Research
- Keywords: AI, tools, Elicit, models, TDM
- Context: Explores AI applications for academic workflows, from literature review tools (Elicit, Scite) to text mining (TDM).

Visualizations
- The 2D cluster chart demonstrated clear separation between topics, indicating strong thematic distinctions.
- The word cloud highlighted the prominence of terms like “data”, “open” and “HKUST”, reinforcing key themes.

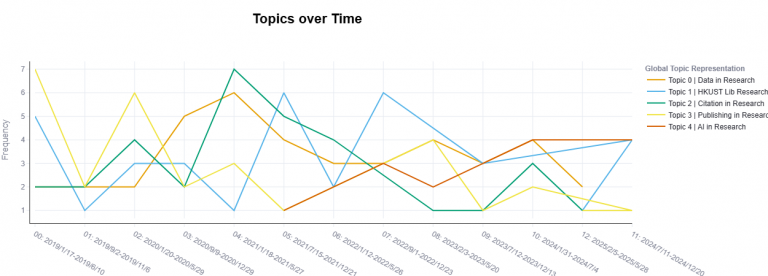
Topic Trends Over Time
We also examined how blog topics evolved from 2018 to 2025:
- Citation & Academic Integrity peaked in early 2021, coinciding with updates to major citation styles and university-wide integrity campaigns.
- AI & Emerging Technologies emerged as a dominant theme starting in late 2021 onwards, mirroring the broader academic interest in AI tools like ChatGPT.
The chart below illustrates these trends, with distinct lines representing each topic’s prevalence across the years.
Challenges & Lessons Learned
- Limited Data: The small number of posts led to fewer topics. We prioritized coherence over quantity.
- Randomness in Modeling: Small datasets can lead to variability; setting a minimum topics parameter helped stabilize results.
- Engagement Correlation: We explored links between topic types and blog views, but the data was too sparse to draw firm conclusions. A larger sample would increase reliability.
Conclusion
This project showcased the power of topic modeling to uncover hidden patterns and inform strategic decisions, even with limited data. The five identified topics provided actionable insights for the Research Bridge Blog editing team, from optimizing tags to guiding future content creation.
For researchers and librarians, our findings highlight the value of data-driven approaches in understanding academic discourse. We invite others to explore our Topic Modeling Tool and collaborate on similar projects!
By continuing to refine these methods, we can further bridge the gap between data science and library sciences, fostering a more insight-driven academic community.






