Writing the text for the project Tales from a 1493 World Map: Playing with Augmented Reality (AR) was meant to be a straightforward task - just a bit of history, a touch of mythology, and voilà, a finished story. In reality, it turned into a full-scale expedition through time, culture, and a bestiary of fantastical creatures that make Godzilla seem downright tame. Though my journalism background prepared me for chasing deadlines and digging for facts, tackling a 1493 German medieval map brimming with monsters borrowed from Greek, Roman, and other mythologies was an entirely different challenge. Let’s just say neither history nor myth was accompanied by a user guide. For an entire month, Tory, the Head of the library’s Research & Learning Support, and I became part-time historians and mythical creature specialists. We scoured the HKUST library as if it were a treasure trove, navigating dusty tomes and digital archives from museums across Europe and North America. We encountered ancient manuscripts, encyclopedias, and artistic interpretations that looked like the creative output of medieval monks during a very long sermon. The greatest challenge? Distinguishing fact from fiction - or, as I came to call it, playing medieval myth-whack-a-mole. One source portrayed a beast as a noble fire-breather; another insisted it was merely an irritable lizard with attitude problems.
What's Up on the Ground Floor this September? You may have noticed something unusual just inside the G/F gates of the Library. What is it? A display of a digital humanities project for you to interact (play) with. What's the story? In spring semester 2025, 5 UG students worked with library staff as one of the DS CoLab projects to bring a 520 year-old map from the Library's collection to life. They used augmented reality (AR) technology to create an engaging and interactive visual way to explore the cultures and histories that went into the creation of "Secunda etas mundi", The Second Stage of the World, from Hartmann Schedel's Nuremberg Chronicle (1493). This map is a fascinating piece from the library’s Special Collections. It shows “The Second Age of the World” (out of 6), the stage between Noah’s Flood and the birth of Abraham. These ages were a periodization of world history (common in Christian Europe for about 1,000 years), first formulated by the North African Christian theologian, Augustine of Hippo (354-430 CE). A remarkable example of late medieval cartography, it combines knowledge from the Greek geographer Claudius Ptolemy with visual references from religion and mythology from Europe and the lands surrounding the Mediterranean.
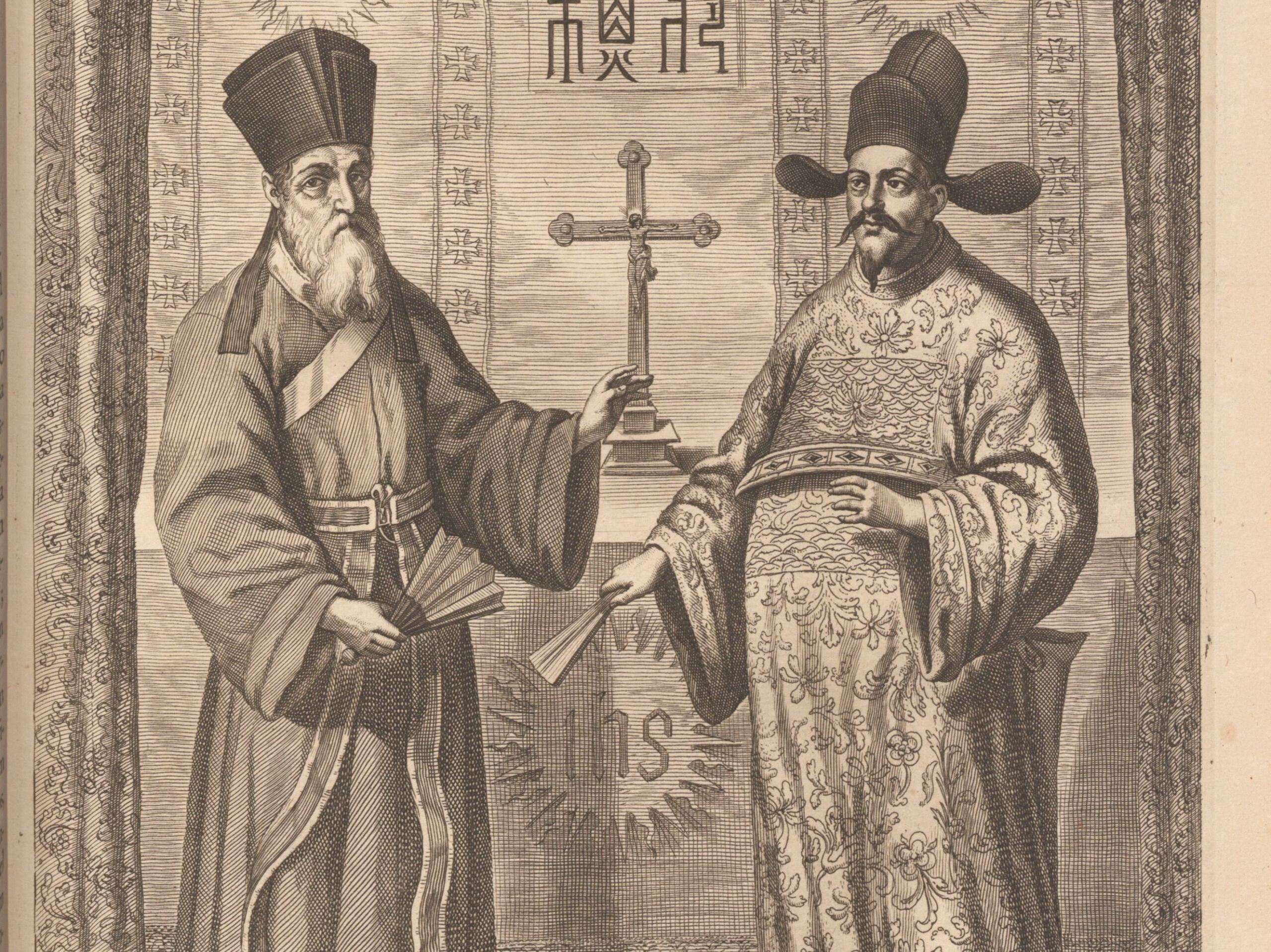
You might have heard the Italian name Ricci – perhaps Ricci Hall, one of the oldest residential halls at HKU. But do you know who Matteo Ricci was? The man who made this Italian name famous in China. Who was Matteo Ricci? Matteo Ricci (1552-1610) was one of the first Jesuit missionaries who tried to spread Christianity in China. He was born in Macerata, a small town in central Italy with a population of just under thirteen thousand. At the age of 20, Ricci was admitted to the Roman College, a Jesuit university renowned for its expertise in natural philosophy. Hmm, what exactly was natural philosophy? Mathematics, astronomy, music, geography, and more technical disciplines like mechanics and architecture. For example, how to craft a globe?
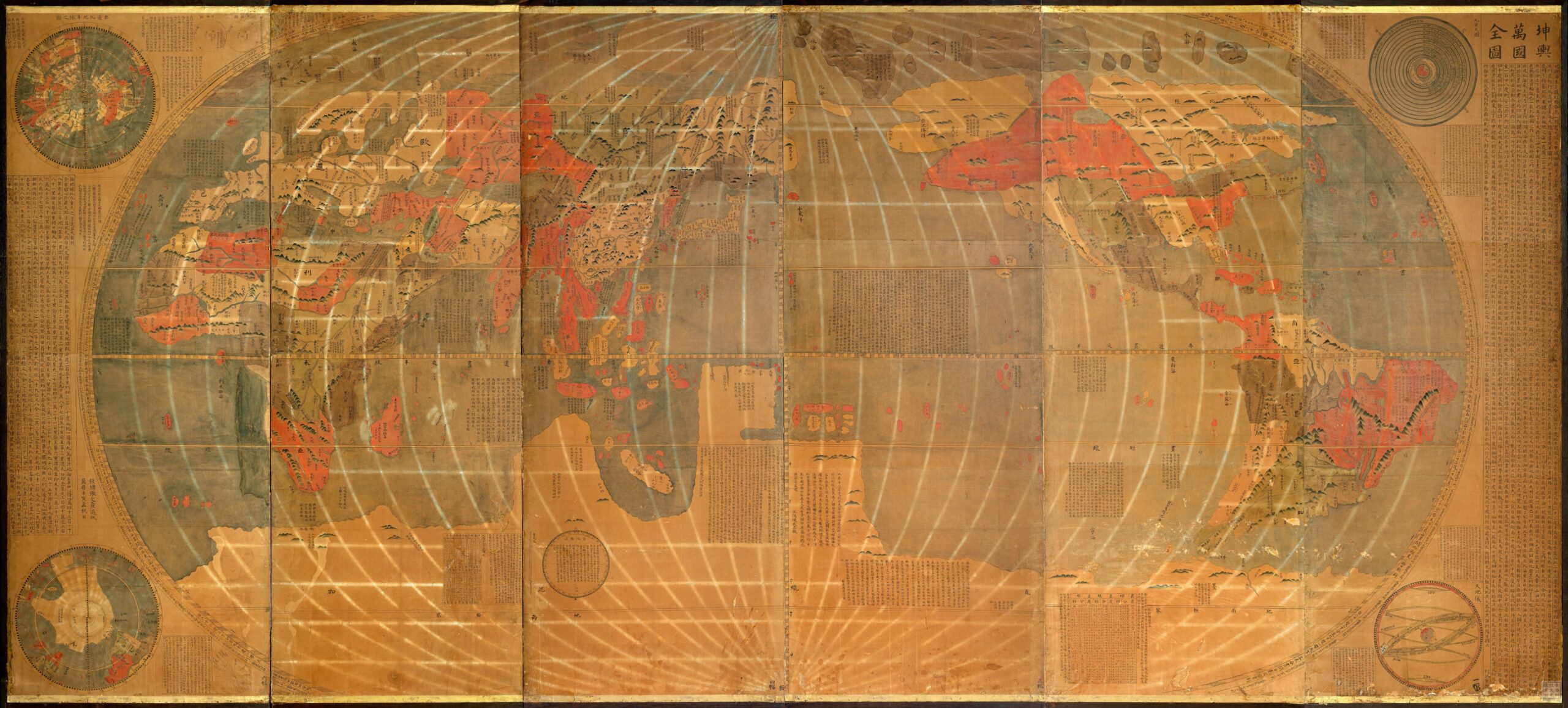
Did you know this is one of the most glamorous items in our Special Collections? Known as 坤輿萬國全圖, in elegant classical Chinese, literally meaning Map of the Ten Thousand Countries of the Earth, it also has a nickname in English – Ricci Map. Why Ricci in English? Why does this map, titled in Chinese, carry an Italian name in the English-speaking world? It’s an attribution to the mapmaker, Matteo Ricci (1552-1610). He was an Italian missionary of the Society of Jesus and one of the first Jesuits to arrive in Ming China. At the imperial court of Emperor Wanli 萬曆, he served as an expert in astronomy, geography, and mathematics. His map is the first world map based on European cartography but positioned China at the center of the world. However, Ricci did not create this map alone. He closely collaborated with Chinese scholars and artisans, including Li Zhizao 李之藻 (1565-1630), a scholar-official from Hangzhou.
Old maps are visually beautiful; and they carry a lot of interesting stories. The Library hosted a 3-day research symposium last December with map historians from local and overseas institutions. One really memorable talk in the symposium was about this famous Chinese map dated 1644, the year the Ming Empire collapsed: <天下九邊分野人跡路程全圖> (A comprehensive map of the kingdom of China and neighbouring countries). The speaker, Professor Mario Cams of KU Leuven (Belgium), explained that this fascinating map was a hybrid of Chinese and European mapmaking; he told the interesting threads of history in a century of east-west exchanges that led to this map. We do not have a copy of this rare map, but you can find a similar one printed in the 18th Century in our Special Collections. You can examine the image of the 1644 map at this site: look for the latitude scale, north and south poles, Europe, North and South Americas (separated); these are the typographical knowledge from the West, and are scattered around the edges of the map. However, the bulk of the map in the middle is the Ming Empire administration, which is not intended to represent geographical reality. To weave the story of the map, Professor Cams started in 1555, the era when 2 Chinese maps from Fujian travelled to Europe via merchants in Southeast Asia. Afterwards, Jesuit missionaries brought European geographic knowledge to the East, forming the basis of this "hybrid map". An important thread in the story is the Ming book publishing culture.
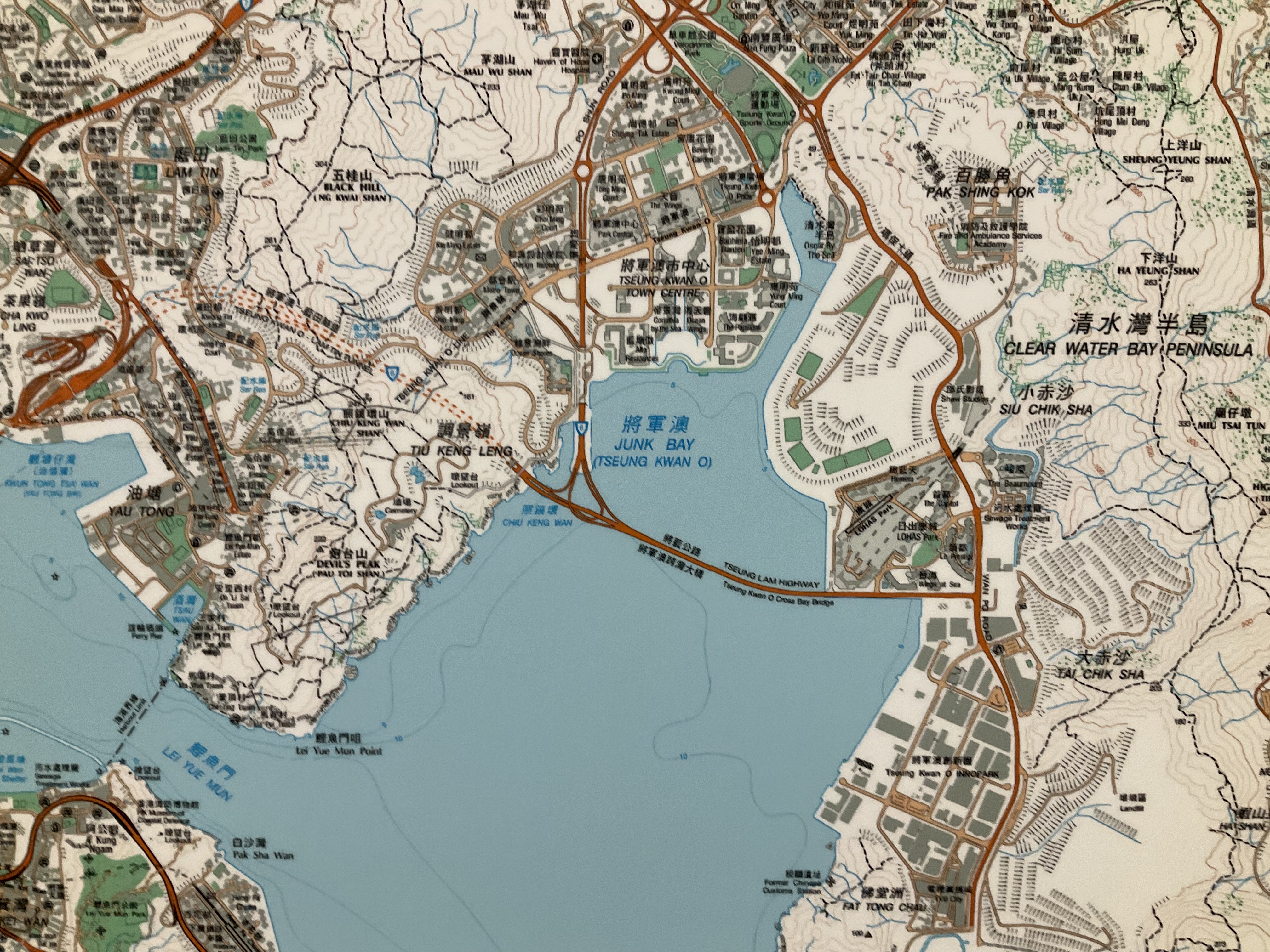
You probably use a Hong Kong map often. When you check a bus route, explore a hiking trail, find your way to a restaurant …, you use a map, most likely a digital one on your mobile device. For a change of perspective, I invite you to look "up" rather than "down" on your phone – come to the Library to experience a large wall map of Hong Kong! The big map is almost 3m x 3m, mounted on a big wall on the G/F. We have had the HK map there for many years, and we recently updated it to the latest version. Not only is the color brighter and the print sharper on this newly printed map, this version has richer details of the city. And of course you can find many new landmarks, such as the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge, the West Kowloon Cultural District, and the Tseung Kwan O Cross Bay Link. Come and experience the physical map offline! See if you find anything new. Happy exploration!
If you haven't checked out the Library Exhibition "China In Maps 500 Years of Evolving Images" yet, you're missing out! This introduction video is just the beginning of an exciting journey. You'll find an excellent example of how students can take their learning to the next level. [embed]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z79oXtpX5xg[/embed] Meet Delores Yip and Felicia Pang, two Year 3 students from the School of Engineering (SENG). They are fast learners with a passion for Minecraft, a game that has captured the hearts of many. With their engineering background and gaming skills, they were able to create an engaging and interactive experience for visitors to the exhibition. This is just one example of the extended learning opportunities available to students at the library. By collaborating with co-curators, students can create compelling storylines that bring history and technology together in exciting ways. So why not join us on this journey of discovery and exploration? Who knows what you might learn!