Writing the text for the project Tales from a 1493 World Map: Playing with Augmented Reality (AR) was meant to be a straightforward task - just a bit of history, a touch of mythology, and voilà, a finished story. In reality, it turned into a full-scale expedition through time, culture, and a bestiary of fantastical creatures that make Godzilla seem downright tame. Though my journalism background prepared me for chasing deadlines and digging for facts, tackling a 1493 German medieval map brimming with monsters borrowed from Greek, Roman, and other mythologies was an entirely different challenge. Let’s just say neither history nor myth was accompanied by a user guide. For an entire month, Tory, the Head of the library’s Research & Learning Support, and I became part-time historians and mythical creature specialists. We scoured the HKUST library as if it were a treasure trove, navigating dusty tomes and digital archives from museums across Europe and North America. We encountered ancient manuscripts, encyclopedias, and artistic interpretations that looked like the creative output of medieval monks during a very long sermon. The greatest challenge? Distinguishing fact from fiction - or, as I came to call it, playing medieval myth-whack-a-mole. One source portrayed a beast as a noble fire-breather; another insisted it was merely an irritable lizard with attitude problems.
What's Up on the Ground Floor this September? You may have noticed something unusual just inside the G/F gates of the Library. What is it? A display of a digital humanities project for you to interact (play) with. What's the story? In spring semester 2025, 5 UG students worked with library staff as one of the DS CoLab projects to bring a 520 year-old map from the Library's collection to life. They used augmented reality (AR) technology to create an engaging and interactive visual way to explore the cultures and histories that went into the creation of "Secunda etas mundi", The Second Stage of the World, from Hartmann Schedel's Nuremberg Chronicle (1493). This map is a fascinating piece from the library’s Special Collections. It shows “The Second Age of the World” (out of 6), the stage between Noah’s Flood and the birth of Abraham. These ages were a periodization of world history (common in Christian Europe for about 1,000 years), first formulated by the North African Christian theologian, Augustine of Hippo (354-430 CE). A remarkable example of late medieval cartography, it combines knowledge from the Greek geographer Claudius Ptolemy with visual references from religion and mythology from Europe and the lands surrounding the Mediterranean.
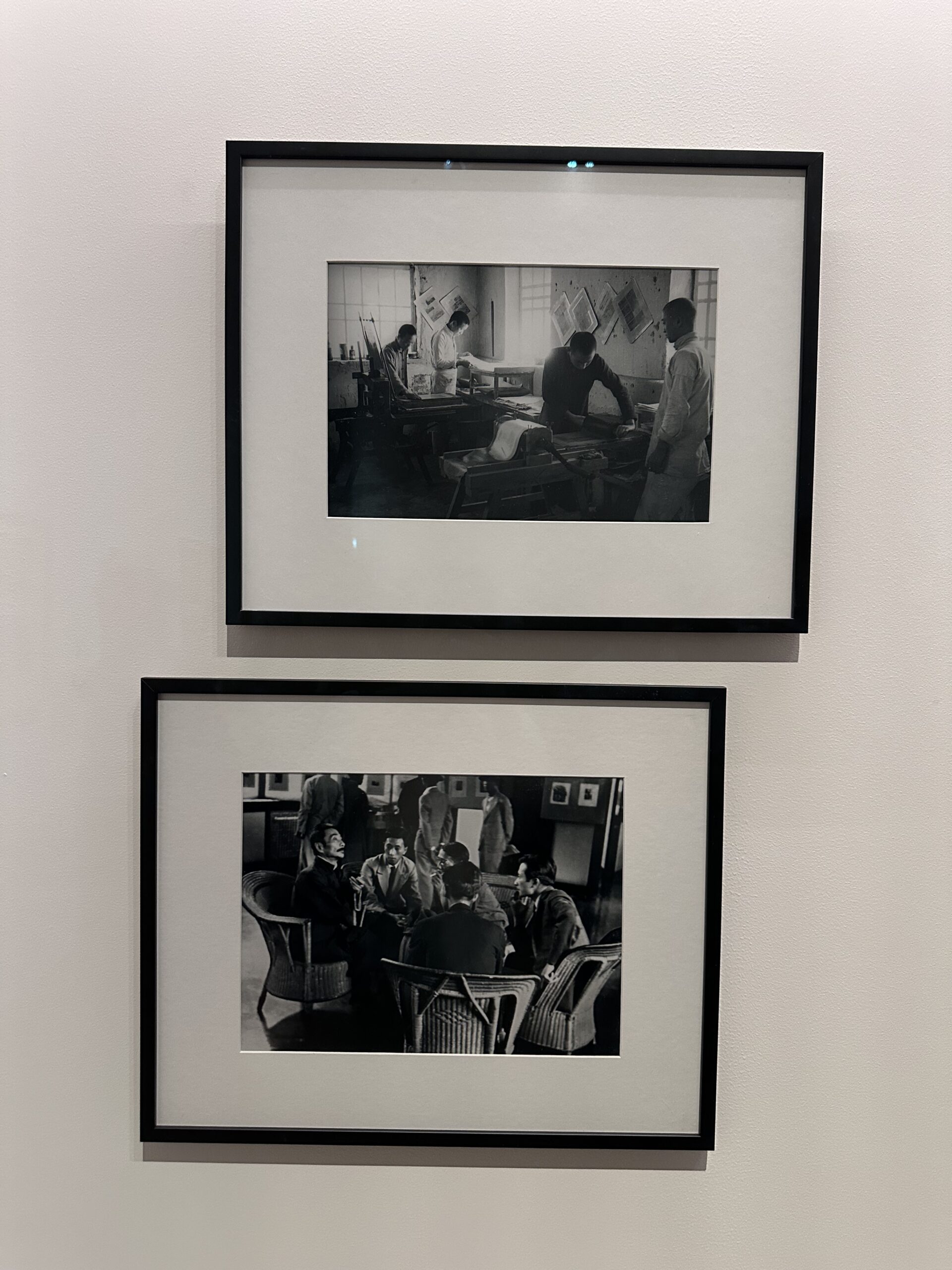
Did you know that Canton (Guangzhou) and Hong Kong, twin cities where Cantonese is the lingua franca, have much more in common beyond language? Modern art and visual culture born in the two cities share a legacy deeply rooted in the history of Modern China. M Museum’s recent exhibition “Canton Modern: Art and Visual Culture 1900s-1970s” showcases over 200 artworks – many on public display for the first time – from this lesser-known history. Sha Fei, a featured artist in this exhibition whose works are on loan from our Library’s Special Collections, is regarded as one of the most influential Chinese photographers of the 20th century. Born and educated in Guangzhou, Sha Fei, originally named Situ Chuan, came from an extended family that was well known for its artistically talented members, including a film director and two painters. Initially aspired to be a fine art photographer, Sha Fei turned his lens towards the working class and later, scenes of war during the 1930s-40s. This transformation was driven by a shared artistic vision among Cantonese artists highlighted in the M exhibition: the belief that art could influence people and transform society. Two of Sha Fei’s works on display at M , photos taken by the author. As a photojournalist, Sha Fei produced more than a thousand photo records of the Sino-Japanese War. Thanks to a generous donation from Sha Fei’s daughter, Ms Wang Yan, who reached us through Professor David Cheng Chang at the Division of Humanities, our Library now holds a collection of Sha Fei’s wartime photographs: Sha Fei Photographic Collection.
As a Hongkonger, I like to browse information about Hong Kong’s past through various media. When I look at posts and photos of Hong Kong’s past, I have an opportunity to see things that remind me of my childhood, which makes me feel excited. In our library, there are many books and periodicals that discuss Hong Kong’s past. Some of them are pictorial works with illustrations of old Hong Kong. They are “Popular books” that enable users to explore Hong Kong’s history through a relaxing journey.
Did you know that the little hill beside the North Gate bus stop has a name? It is called the Fung Shui Ridge! Do you know what its name, "Fung Shui", means? Fung Shui (風水) is the traditional Chinese practice of arranging buildings and spaces. Even thousands of years ago, people understood the importance of the environment on their lives, and sought to improve their living spaces. On a small scale, moving some furniture away from the door or not putting your dining table directly across the toilet is easily doable. But constructing whole mountains to block out cold winds is impossible outside fables. The solution, then, is to simply build around and according to nature. And from these beliefs and actions came Fung Shui, as both a field of study and a way of life. A stranger to Fung Shui may dismiss it as mystical and unscientific.
In a remarkable team effort, the University Archives recently completed installation of a memorial corner dedicated to our late founding president, Prof. Chia-Wei Woo. Did you know that it was Prof. Woo’s vision back in 1990 to establish a university archive for preserving historically significant materials relating to our university? This memorial corner could not showcase such valuable materials without his foresight and commitment to safeguarding our university's history. Within a week of announcing Prof. Woo's passing, our dedicated team collaborated to plan, design, prepare, and assemble a small display at the Library G/F Gallery to honor his memory. Our first step involved selecting items that best reflect Prof. Woo’s connection with the university and his visionary values. Among the treasures selected are three important letters from 1985 and 1987 that mark his appointment as founding president and the university’s founding years.
I was sad to hear the news. He will be missed. I want to share a couple of anecdotes – two of my encounters with him in the early days of the University. I was a very junior staff and only ever knew the President casually, but he knew who I was and always had a smile or a nod. In the early 1990s, HKUST had a dinner party. I don't recall the event - perhaps a staff association function. After dinner, the mahjong tables were set up and somehow I ended up in a foursome with my boss and the President. I warned them I had barely learned how to play and would be slow - but they needed a fourth and there I was. It was enjoyable, especially as we were only playing for points, and low ones at that. There was much talk, and fun, and tea.
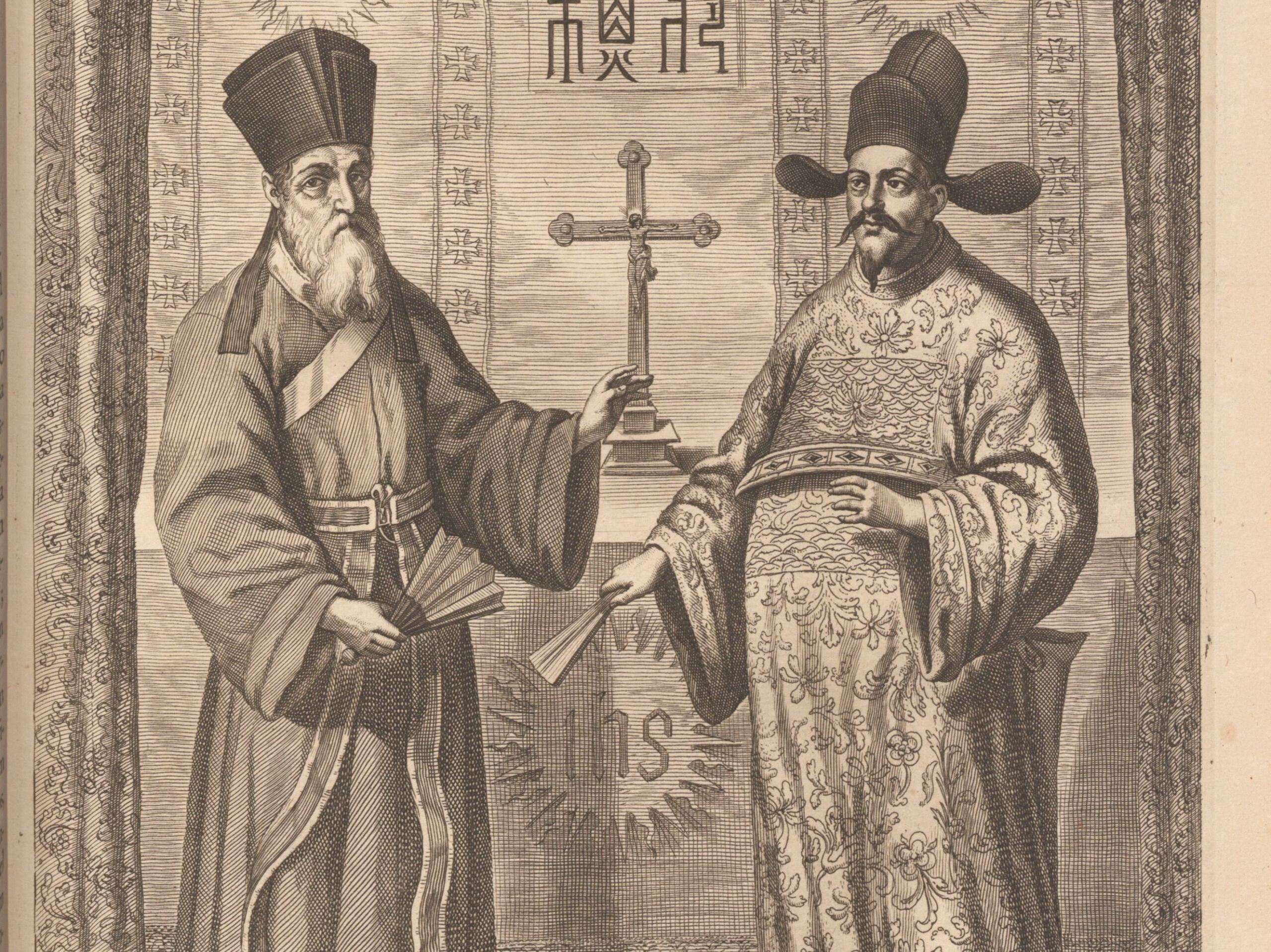
You might have heard the Italian name Ricci – perhaps Ricci Hall, one of the oldest residential halls at HKU. But do you know who Matteo Ricci was? The man who made this Italian name famous in China. Who was Matteo Ricci? Matteo Ricci (1552-1610) was one of the first Jesuit missionaries who tried to spread Christianity in China. He was born in Macerata, a small town in central Italy with a population of just under thirteen thousand. At the age of 20, Ricci was admitted to the Roman College, a Jesuit university renowned for its expertise in natural philosophy. Hmm, what exactly was natural philosophy? Mathematics, astronomy, music, geography, and more technical disciplines like mechanics and architecture. For example, how to craft a globe?
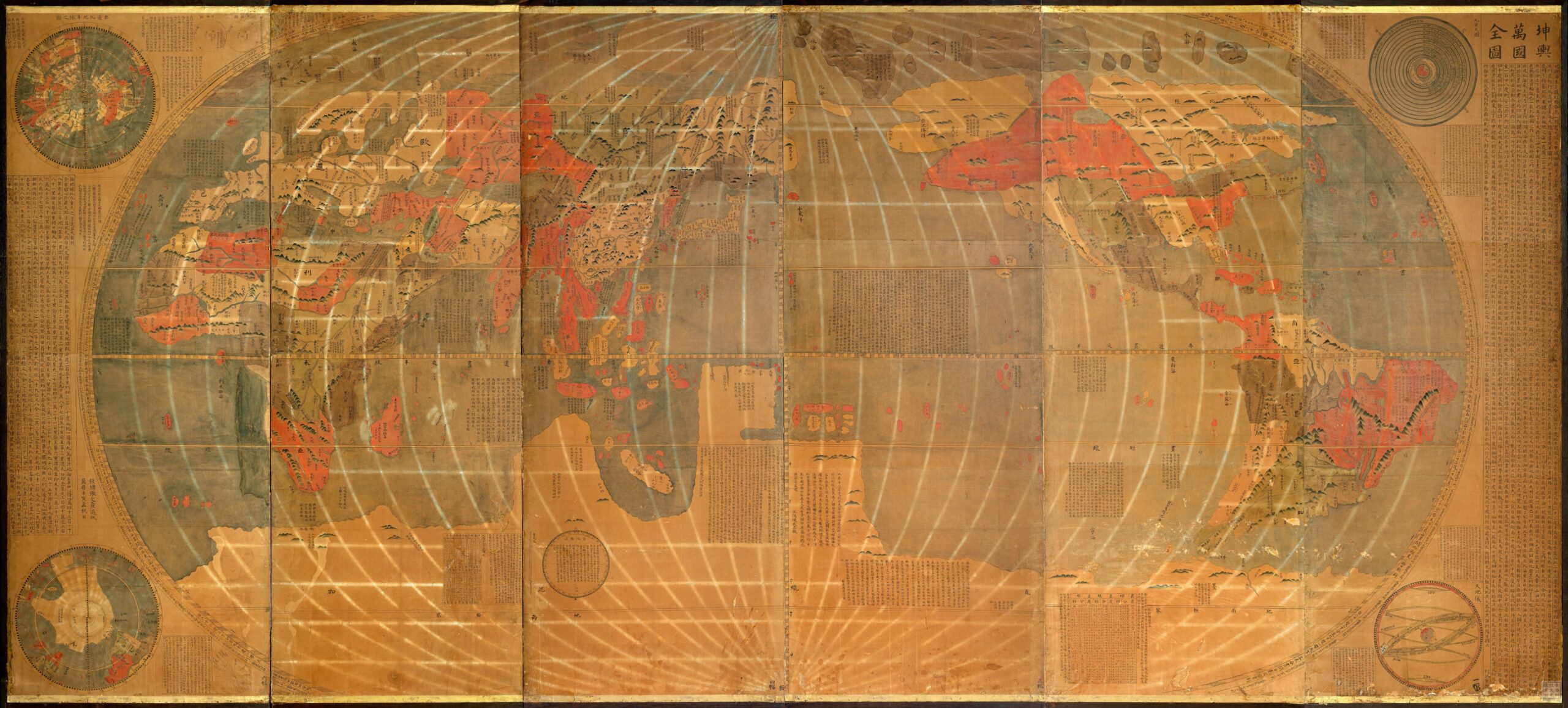
Did you know this is one of the most glamorous items in our Special Collections? Known as 坤輿萬國全圖, in elegant classical Chinese, literally meaning Map of the Ten Thousand Countries of the Earth, it also has a nickname in English – Ricci Map. Why Ricci in English? Why does this map, titled in Chinese, carry an Italian name in the English-speaking world? It’s an attribution to the mapmaker, Matteo Ricci (1552-1610). He was an Italian missionary of the Society of Jesus and one of the first Jesuits to arrive in Ming China. At the imperial court of Emperor Wanli 萬曆, he served as an expert in astronomy, geography, and mathematics. His map is the first world map based on European cartography but positioned China at the center of the world. However, Ricci did not create this map alone. He closely collaborated with Chinese scholars and artisans, including Li Zhizao 李之藻 (1565-1630), a scholar-official from Hangzhou.
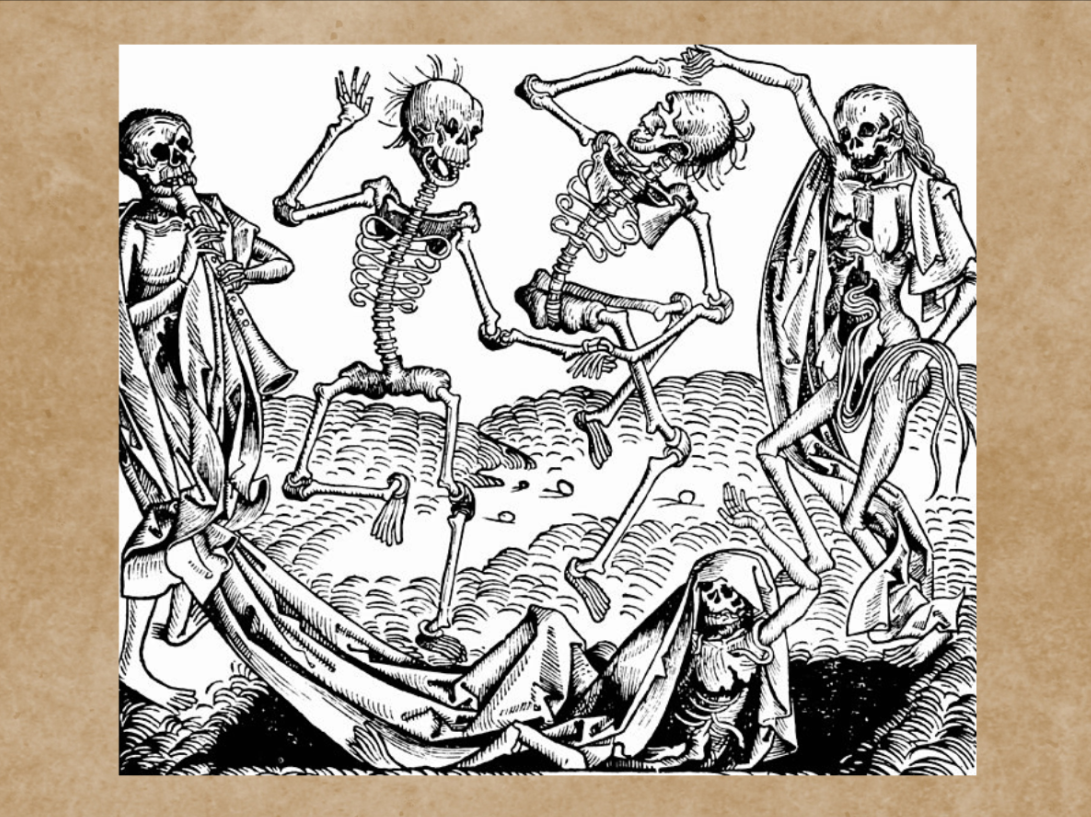
Part 1 discussed how students can fight monsters of anxiety about grades & GPA by laughing and learning with the Wisdom Stone Game. But, some carry around other fears. Since childhood, we’ve become familiar with the idea or cliché of corpses and skeletons coming to life. Others may fear living creatures like spiders or snakes. We get “spooked out” by such things, except when they are silly or pretty. There’s a long tradition of dealing with these fears by confronting or even celebrating them. Here’s an example: Danse Macabre, composed by Camille Saint-Saëns, performed by Lydia Ayers, Andrew Horner, and Stella So. Danse Macabre, also called the Dance of Death, is an allegorical concept said to encapsulate the unconscious fear of death.1 The popularity of the Danse Macabre art such as poetry, music and drama, can be traced back to the 13th century, when Europeans became obsessed with death inspired by the Black Death and the Hundred Years’ War.2 This video of a puppet show, available on DataSpace@HKUST, is part of a collection of the music, and puppet productions of the late Dr. Lydia Ayers, a former professor at HKUST, given by her widower, Dr. Andrew Horner, a professor of Computer Science here.