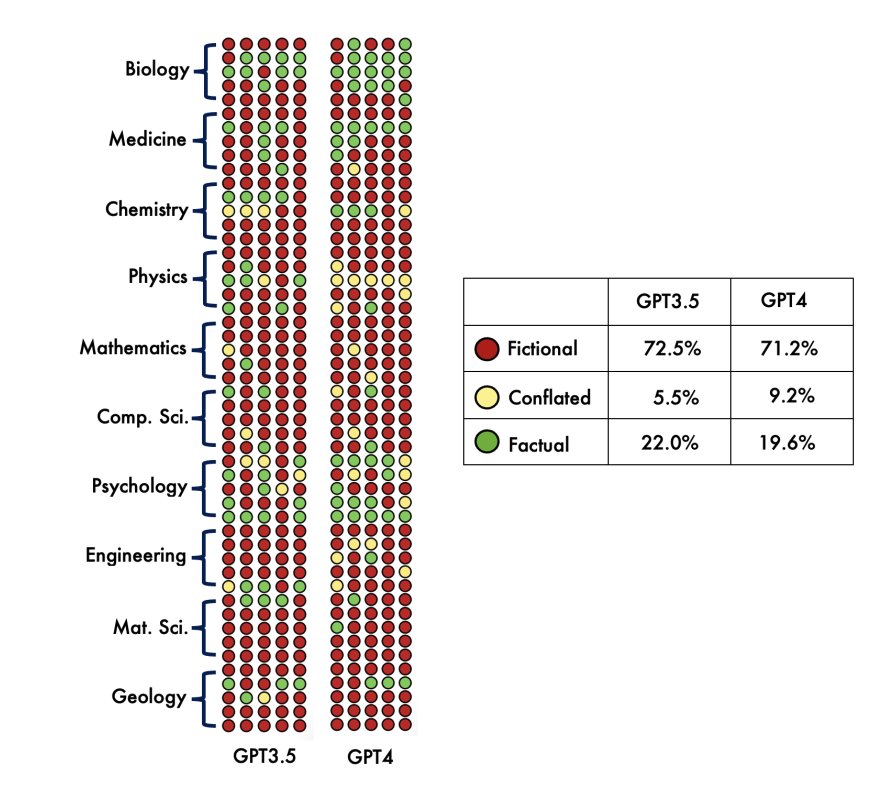
Hallucinations, or the generation of inaccurate or fabricated information, are a significant concern surrounding the use of AI. In this post, we introduce five AI research tools that can generate answers based on real sources. These tools are designed to ensure that students and researchers can rely on accurate and reliable information when citing sources.
|
Scite Assistant
https://scite-ai.lib.ezproxy.hkust.edu.hk/assistant
- Scite.ai offers a conversational AI Assistant that provides answers referencing real papers with real DOIs.
- Sentences of the referenced part are highlighted from their full-text so we can see where and why they are relevant.
- Users have control over the Assistant's setting, such as specifying reference sources (from certain journals or Scite dashboards), reference year range, and the number of references to include in an answer.
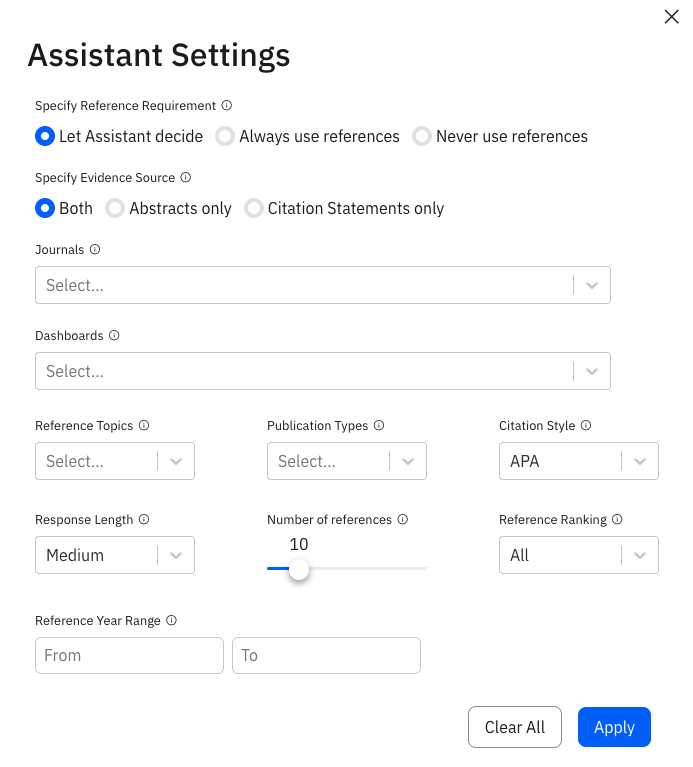
Users can specify their reference requirements in the settings of Scite Assistant.
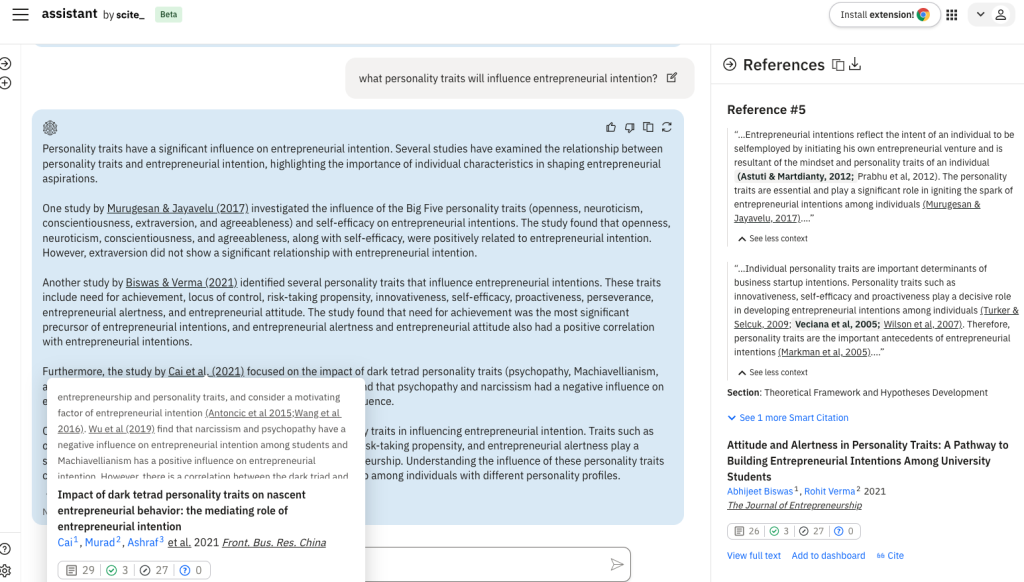
Scite Assistant provides real sources, and when clicking on the sources in the answer, users can view relevant citation statements, as well as the source’s Smart Citation metrics.
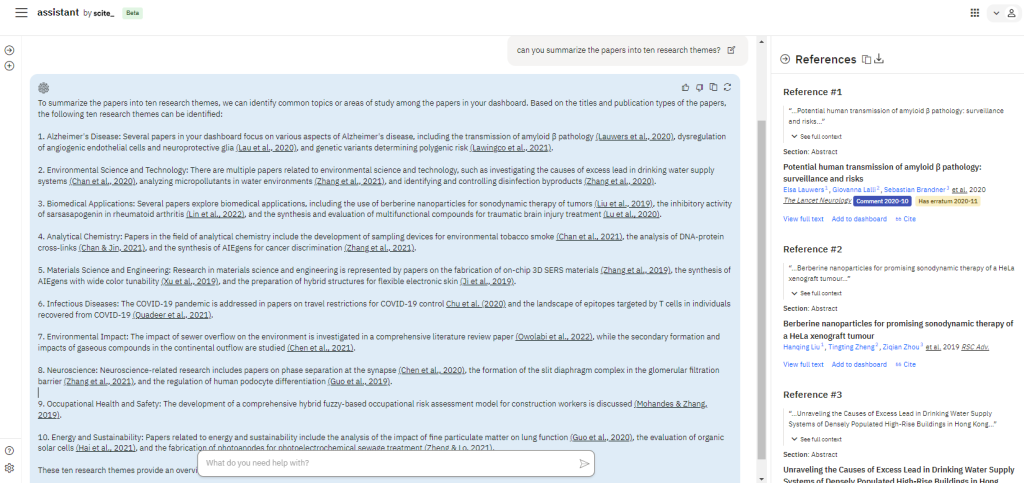
I have a Scite dashboard of around 900 papers which are HKUST publications on SDG#3 "Good Health and Well-Being" between 2019 and 2022. Scite Assistant helped to summarize the papers into ten research themes and highlighted key papers.
SciSpace
- Similar to Scite Assistant, SciSpace allows users to refine results based on publication type, year, or towards a specific PDF.
- The SciSpace Copilot Chrome extension is a convenient tool for answering questions and explaining concepts in a paper while browsing the web.
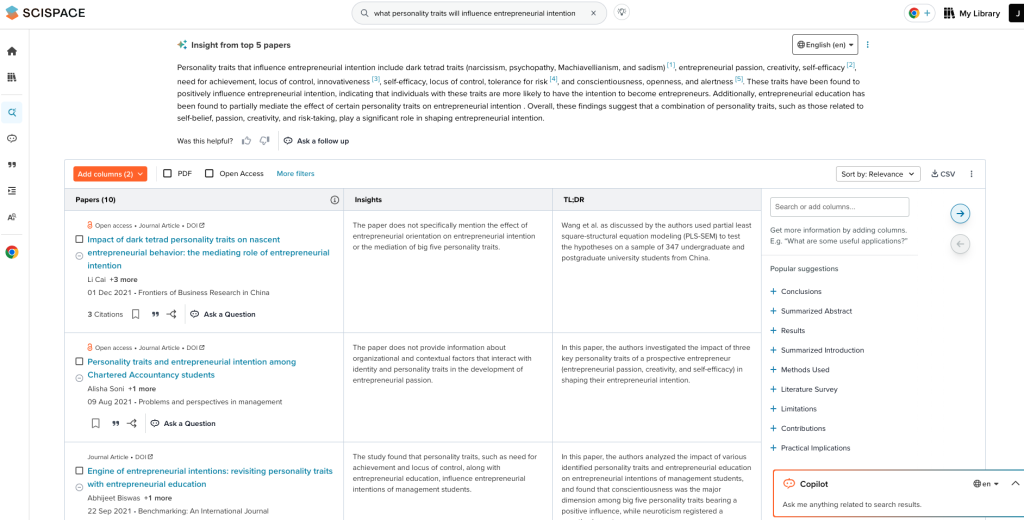
A mini-literature review on a research topic, where referenced papers are summarized into a structured table.
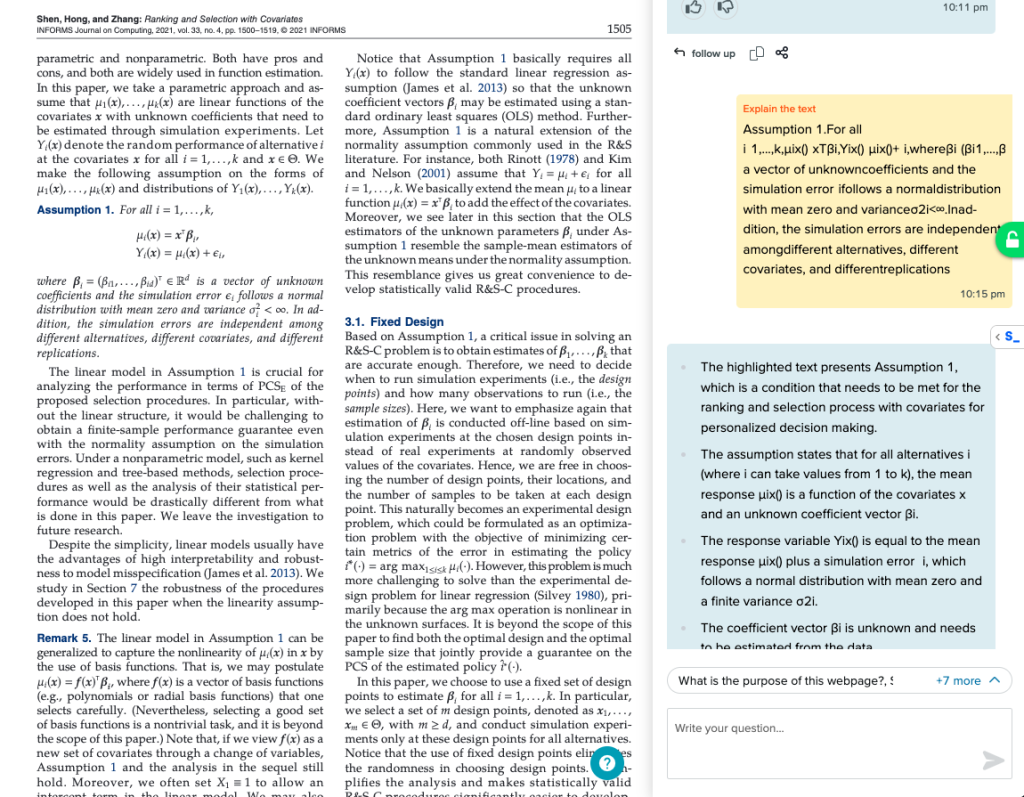
The copilot plugin can answer questions from a paper and explain highlighted text, including mathematical concepts.
Elicit (Beta)
- The beta version of Elicit.org supports more research workflows and offers more robust results.
- Users can find papers related to their research question, extract information from PDFs, and discover concepts across papers.
- Elicit provides structured tables summarizing relevant papers and allows users to customize and add additional details to the table.
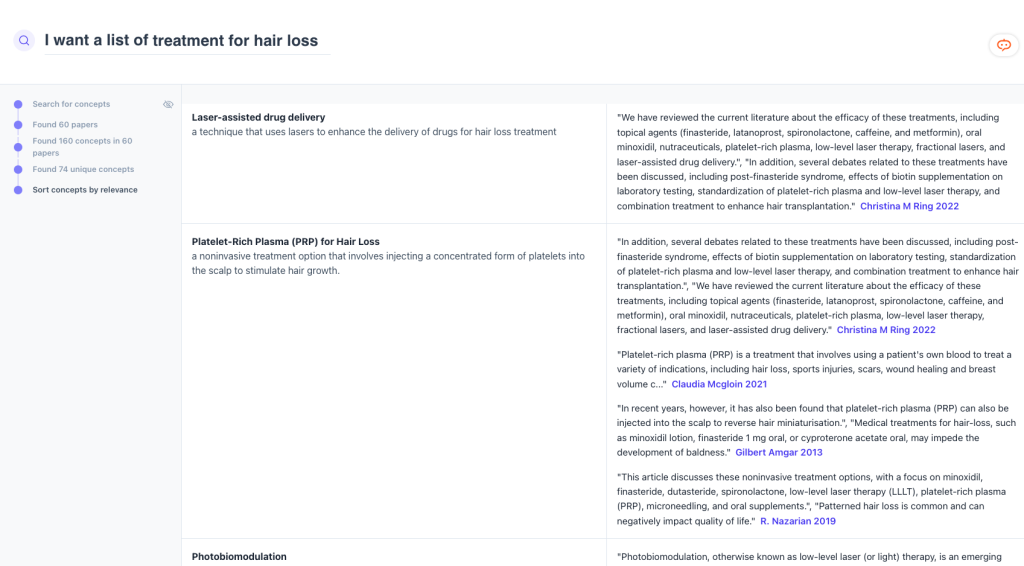
Elicit can identify concepts from relevant papers. As shown on the left-hand of the screen cap, Elicit is relatively transparent by showing the number of papers analyzed to generate the results.
Elicit answers questions based on top relevant papers, presenting them in a structured table. Users can add more columns to the table and indicate key papers. Afterwards, the generated summary may be re-computed accordingly.
Petal
- Petal is a document analysis platform that goes beyond analyzing a single PDF.
- It can answer questions and facilitate multi-PDF chat, allowing users to generate structured AI tables summarizing multiple PDFs.
- Petal offers flexibility in customizing the columns of the AI table and allows users to edit cell information if the AI generates inaccurate results.

Similar to SciSpace Copilot, the Petal PDF AI chatbot that can answer questions from a paper, even citing the specific page numbers.
More flexibility in generating AI tables for documents added to the library. Users can edit columns and cell information to correct any inaccuracies.
Consensus
- Consensus positions itself as an academic search engine rather than a chatbot.
- Users can ask research questions, and Consensus synthesizes results from top relevant research papers.
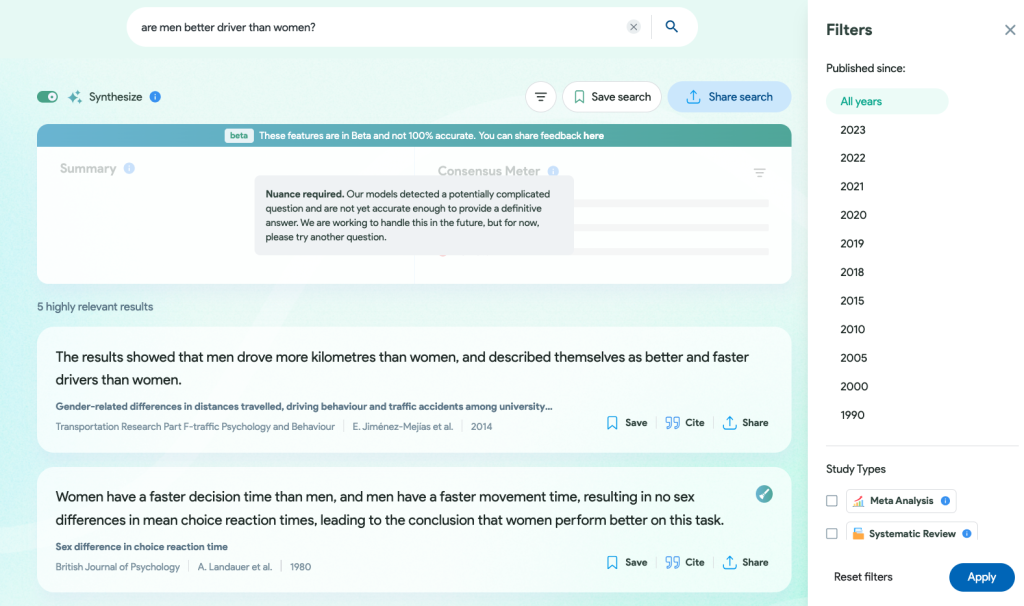
In this example, it recognizes the complexity of the question "are men better drivers than women?" and acknowledges its limitations. However, it still finds five papers and highlights relevant findings.
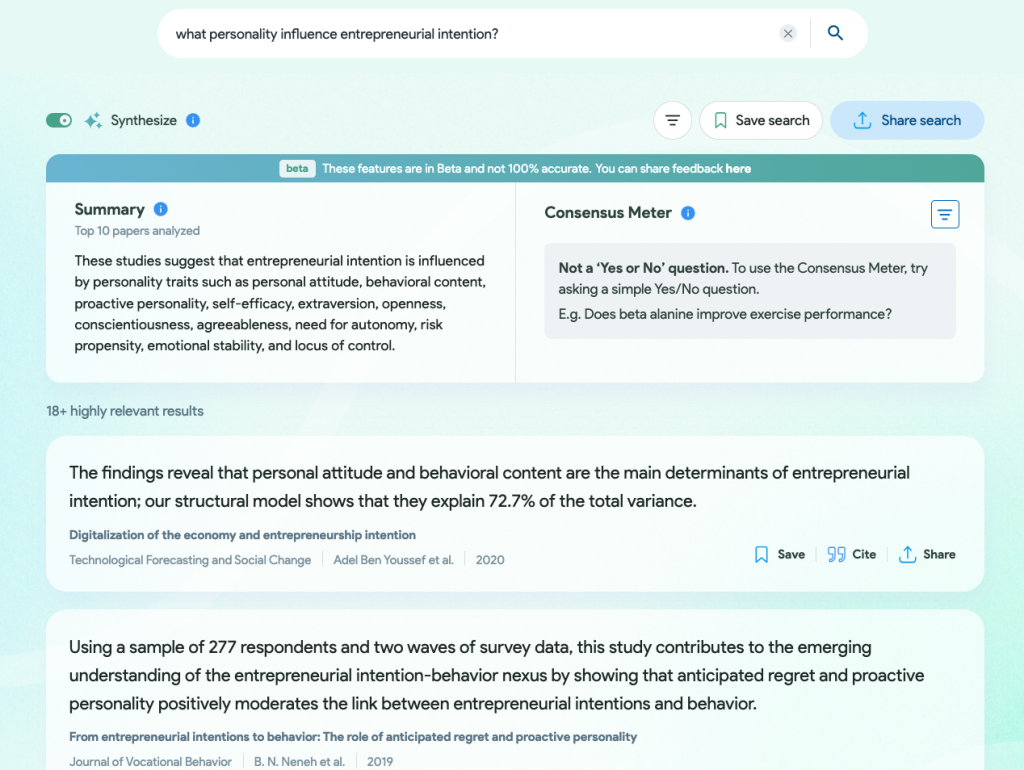
In this example, Consensus does give a synthesized summary base on top 10 papers. It is concise and brief compared to other tools discussed in the post.
Remarks
This post focuses on highlighting the tools' capabilities and is not an exhaustive technical review. It is important to refer to the tools' respective documentation for detailed information about the underlying language models used, data sources, privacy policies, and other specifications. Finally, let’s conclude this post with a table of key features of these tools:
| Scite Assistant | SciSpace | Elicit Beta | Petal | Consensus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Can accept full text PDF upload? | ||||
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Can summarize papers in structured table (lit review matrix)? | ||||
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Can refine/customize reference sources? | ||||
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Can ask chatbot specific questions on multiple papers? | ||||
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Pricing Model | ||||
| Monthly/ Yearly | Monthly/ Yearly | Token | Monthly/ Yearly | Yearly |
| FAQ / About / Support | ||||
| FAQ | FAQ | FAQ (to elicit) | Documentation FAQ | How it Works |