
Altmetrics is an emergent way to assess research impact. Knowing what it means and how to use it is helpful for you to manage your research output and profile.
On article pages in journal websites or repositories, you may have encountered images like these:


What are they? What do they mean for you as a reader or an author?
The Idea of Altmetrics
What is the impact of a research look like? Traditionally, academia judges the quality of a published work by where it is published (Journal Impact Factor), and how often it is cited by others (citation counts, h-index). Citation-based metrics captured a single aspect of a paper’s impact; it takes relative long time to appear.
Scholars use the web as their workspace. If a paper is bookmarked by many peer researchers in reference managers such as Zotero and Mendeley; or many people share the article link with friends in Twitter and Facebook; wouldn’t that paper be considered influential? Altmetrics, the alternative metrics, is a diverse group of measurements that trace a variety of online activities, expanding our views of what count as research impact.
The Key Aggregators in Current Market
To collect a wide range of online traces of citing, quoting, sharing, mentioning, many algorithms and scripts are involved. Currently there are two major companies that aggregate data from the web to compose altmetrics; each of them have their own scope and coverage:
Almetric
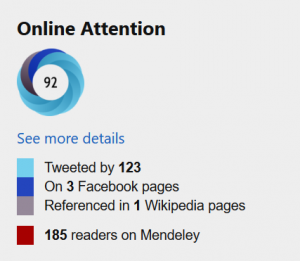
It tracks multiple sources, including:
- References in public policy documents
- Coverage in mainstream media such as news channels and newspapers
- Online reference managers
- Wikipedia citations
- Patents references
- Academic and non-academic blogs
- Research highlights from F1000Prime.
- Social media
It presents data as a “donut” badge, with an overall attention score, and detail breakdown of various counts.
PlumX Metrics
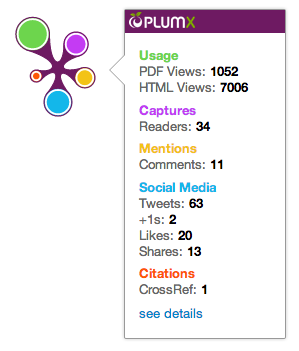
Offered by Plum Analytics, the metrics come in 5 separate categories:
- Citations – traditional journal citation, clinical or policy citations
- Usage – clicks, downloads, views, library holdings
- Captures – bookmarks, code forks, favorites, readers
- Mentions – blog posts, comments, reviews, Wikipedia references, news media
- Social media - shares, likes, comments, tweets
The data is visualized as a Plum Print, color-coded with the five categories.
How to Use Altmetrics
Compare to citation-based measurement, altmetrics are more diverse and quicker to accumulate. They apply not only to books and journal articles, but other research entity such as datasets, software, presentations, researchers and even organizations.
Altmetrics can help researchers to see nuances of research impact. For example, where a paper gets frequently shared, whether a research is getting newspaper coverage, and, what public policies are influenced by the research. These present a richer picture of impact than a single numeric citation counts, which only reflects impact within academic reporting. Metrics aggregated at the author level can help researchers showcase their own impact.
Although you can see some metrics embedded in sites such as the HKUST Institutional Repository and SSRN; getting the full metrics requires subscription. If you are interested to explore altmetrics, contact the Research Support team at the Library or any subject librarians.







