Metadata, or “data about data”, is a critical component of research data management that provides information about a dataset, object, or resource, including its format and collection details.
When describing your research datasets, elements such as titles, descriptions, keywords, size, and date of creation play a crucial role in making your research more findable and easier to understand.
In DataSpace@HKUST, the institutional data repository, datasets may contain multiple data files and corresponding descriptive metadata. When depositing your dataset, the system prompts you to fill in the metadata fields it supports. The more fields you fill in, the easier it is for others to find and reuse your data.
In this post, we provide recommendations to some key metadata fields that can aid in data discovery and reuse.
Identifier
The importance of a persistent ID (PID) goes beyond saying. DataSpace@HKUST assigns a Digital Object Identifier (DOI) to each dataset upon publication. When inputting author information, it is also recommended to include the author’s ORCID to ensure accurate attribution.
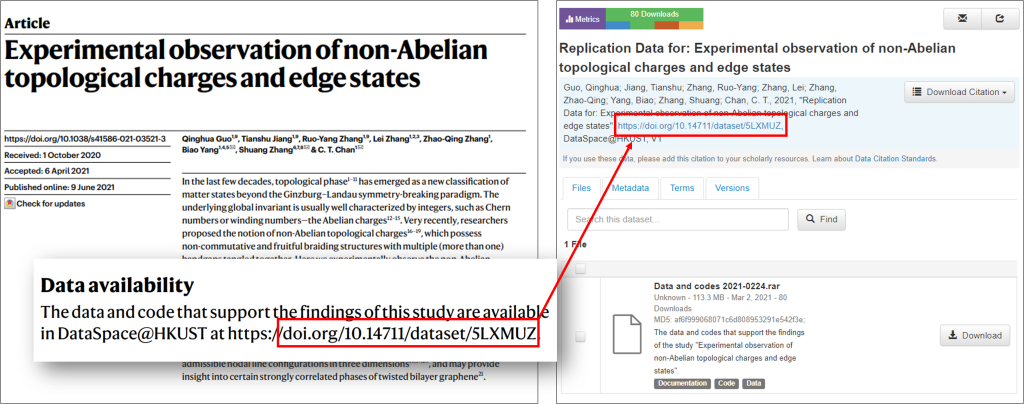
More and more publishers require the provision of data availability statements in their publications. In this example, the authors include a dataset in DataSpace@HKUST with its DOI.
Keyword
Under the current implementation of Dataspace, the keyword field allows free text so users can add any relevant terms. However, it is helpful to adhere to community-specific standards, such as MeSH subject headings for medical and health topics, and the Library of Congress Name Authority File (NAF) for standardized forms of names of persons and organizations. You can browse and search relevant subject vocabularies and terminologies from platforms such as BARTOC (Basic Register of Thesauri, Ontologies & Classifications) and FAIRsharing.org.

Using FAIRsharing.org to search for standards that apply to architecture studies.
Related Publication
This metadata field is dedicated to associated publications, allowing users to link resources and increase the visibility of related publications, such as those that build on or reuse the dataset. It’s important to regularly update this field as the list of related publications grows.
Terms of Use (Rights)
The Terms of Use section is where users can include information about the data’s content license, such as CC0. This information helps researchers quickly determine whether the data is something they’ll be able to use.
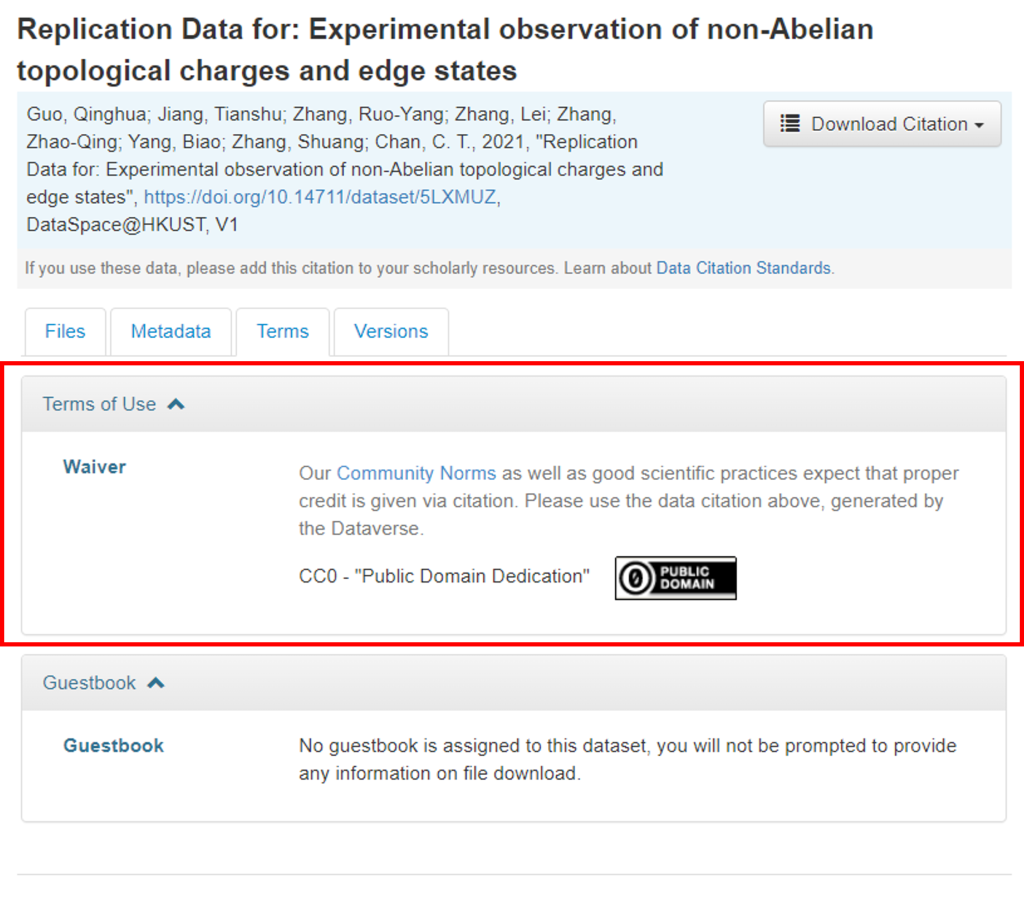
This dataset in DataSpace is licensed as CC0, the least restrictive type of Creative Commons license, which allows for full flexibility of data reuse.
In addition to the best practices we’ve covered in this post, it’s worth taking a look at the FAIR Principles, a set of guidelines for research data management that are relevant not only to metadata, but also to the research data and supporting infrastructural elements. The FAIR principles emphasize the importance of making data findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable. Applying these principles to your dataset will help others find, cite and reuse your data more easily. You can use this self-guided tool to test your knowledge and practices on data management.
Lastly, I would like to showcase a few datasets on DataSpace as examples. Take a look and deposit your own datasets as well!
- China Government Employee Database-Qing (CGED-Q) Jinshenlu Public Release
- Urban Cultural GIS Data of Republican Beijing
- Replication Data for: Experimental observation of non-Abelian topological charges and edge states
– By Jennifer Gu, Library
Views: 1008
Go Back to page Top
- Category:
- Research Data Management Tips
Tags: Data Repository, dataset, description, FAIR principles, metadata, terminologies
published March 10, 2023


