
Earlier this month, the Allen Institute for AI (Ai2) introduced OLMoTrace, a tool that traces LLM outputs back to their multi-trillion-token training data in real time.
For researchers and librarians, OLMoTrace is transformative. It opens a window into an LLM’s “learning” process, allowing us to verify the origins of its outputs, assess how information is synthesized, and answer the critical question, “Where did you learn that?”
Use Cases
OLMoTrace can be accessed via the Ai2 Playground and is available with three models: OLMo 2 32B Instruct, OLMo 2 13B Instruct, and OLMoE 1B 7B Instruct. Ai2’s blog highlighted the following use cases of OLMoTrace:
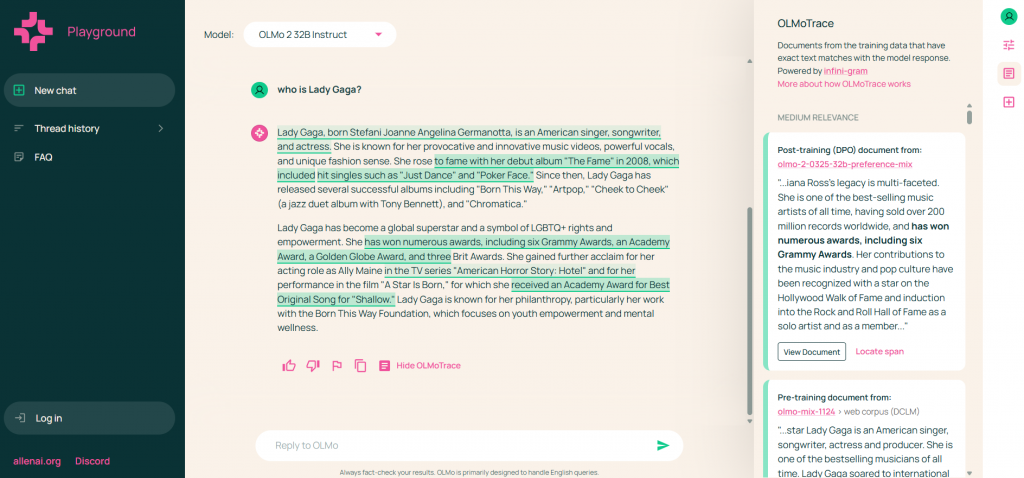
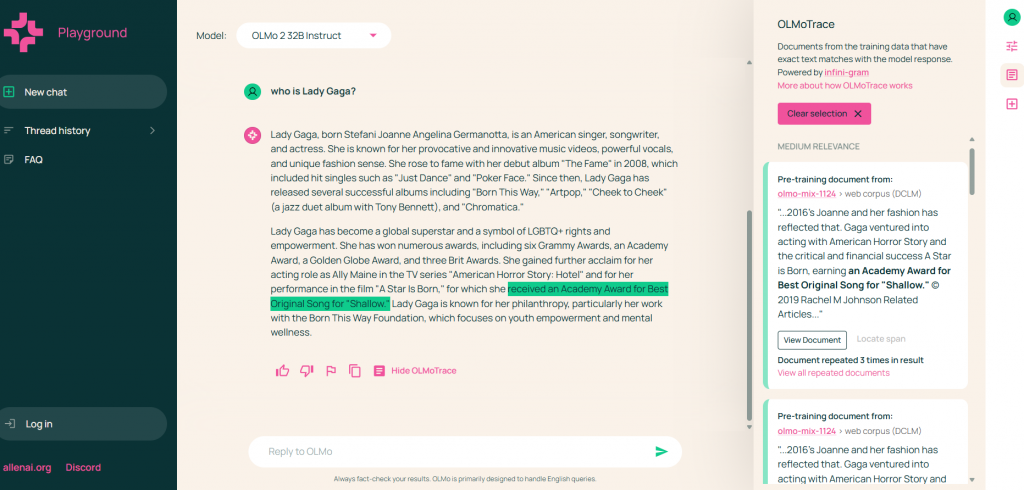
- Fact-Checking: OLMoTrace links model outputs to training documents for verifying factual claims. For example, a sentence about Lady Gaga’s career can be traced to trusted sources in the training data.
- Uncovering Hallucinations: By flagging outputs without verbatim matches, OLMoTrace reveals potential hallucinations - a persistent LLM challenge. For example, Ai2 traced a false August 2023 knowledge cutoff claim in their 13B model to post-training data, enabling refinements to the 32B model and showcasing its debugging power.
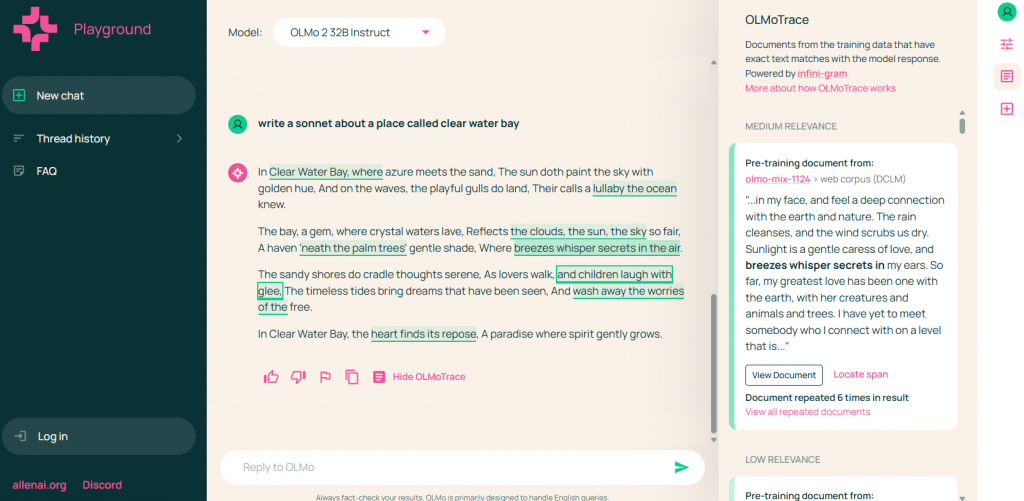
- Tracing Creativity: For creative tasks like writing, OLMoTrace shows whether expressions are novel or derived from training data, aiding researchers studying AI’s creative capabilities.
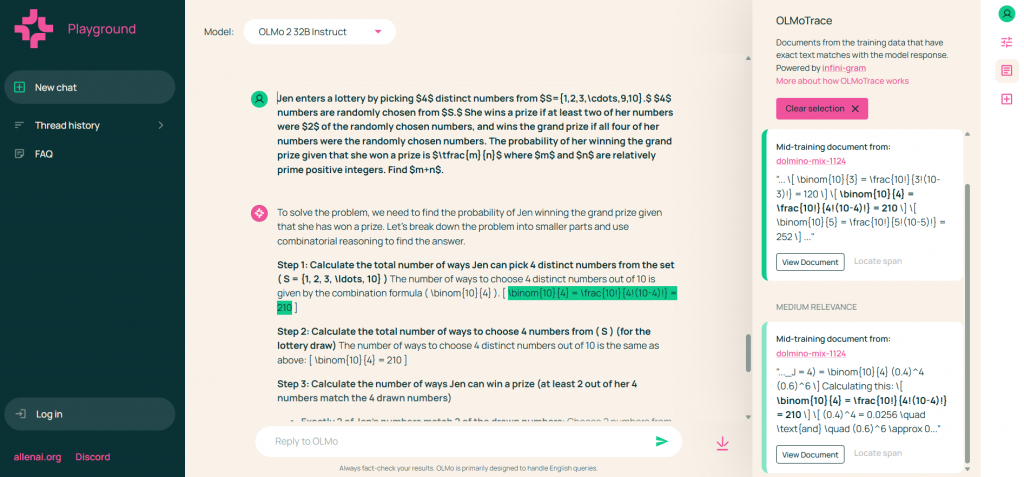
- Mathematical Reasoning: OLMoTrace can show if a model’s solution to a math problem, such as a combinatorics question, is memorized from training data, clarifying reasoning processes.
Behind the Scenes
OLMoTrace’s technical innovations, detailed in Ai2’s paper on arXiv, are what make its real-time tracing feasible. Basically, it scans outputs for “long and unique” text spans matching the training corpus, guided by three criteria:
- Existence: Spans must appear verbatim in the training data.
- Self-Contained: Spans exclude periods or newlines (unless at the end) and avoid incomplete words for meaningful matches.
- Maximality: Spans are the longest possible, not substrings of other matches.
After identifying spans, OLMoTrace ranks them by “span unigram probability” (a measure of rarity, with lower scores for unique tokens) and selects the top 5% for highlighting. Up to 10 documents per span are retrieved, with overlapping spans merged and relevance shown by highlight shades (darker for higher relevance).
Searching 4.6 trillion tokens across 3.2 billion documents is compute-heavy, but two innovations make it feasible:
- Infini-Gram Indexing: Enables fast corpus searches, like finding a needle in a haystack.
- Reduced Complexity: A parallel algorithm cuts the time complexity of span finding from the naive O(L^2 * N) to O(L * log N) (L = length of model output, N = size of training data).
Fostering Trust Through Transparency
Different from retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems like Perplexity, which use external sources, OLMoTrace traces outputs directly to the model’s training data, offering tangible transparency in language models. This distinction makes OLMoTrace suited for auditing and regulatory compliance in fields like healthcare and finance, where trust is paramount. Open-sourced under the Apache 2.0 license, OLMoTrace is adaptable for any model as long as the service provider has access to its full training data.







