Named after the ancient Library of Alexandria in Egypt, OpenAlex is an index of hundreds of millions of interconnected entities across the global research system.
Goodbye MAG and Hello OpenAlex
OpenAlex was launched on 3 Jan 2022 as a replacement for Microsoft Academic Graph (MAG) and it serves as a new free alternative to subscription-based platforms such as Scopus, Dimensions and Web of Science. OpenAlex is run by OurResearch with funding from Arcadia. As of Microsoft Academic (previously we blogged about this) and MAG which hosted the underlying data, some of you may already know that they have all been retired by the end of 2021.
Entities – The Things that OpenAlex is Made of
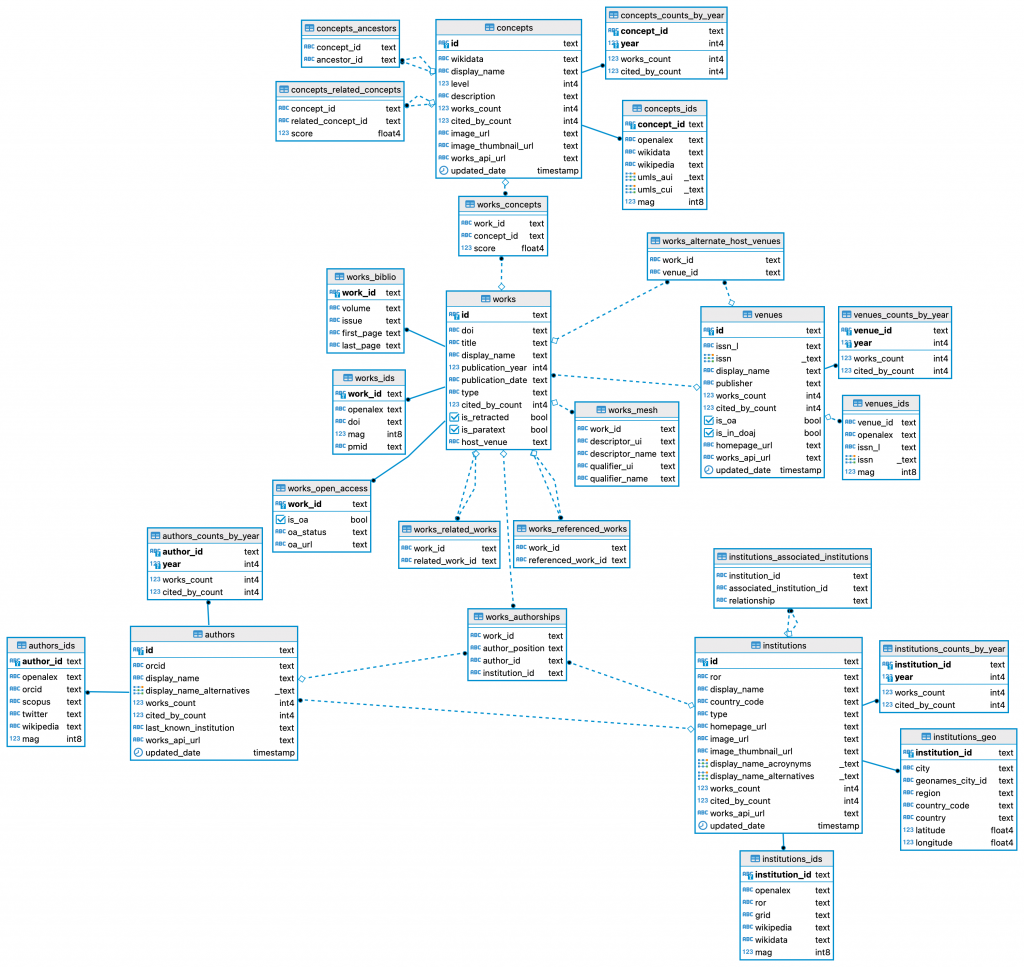
The OpenAlex dataset describes scholarly entities and how those entities are linked to each other. There are five types:
- Works are papers, books, datasets, etc; they cite other works
- Authors are people who create works
- Venues are journals and repositories that host works
- Institutions are universities and other orgs that are affiliated with works (via authors)
- Concepts tag works with a topic
If you think of OpenAlex as a relational database, the schema could look something like the diagram shown below. As of Feb 2022, there are over 200 million works indexed in OpenAlex, hence we can see that this database essentially is a huge web of hundreds of millions of entities and over a billion connections between them all.
Data Source
OpenAlex aggregates and standardizes data across a myriad of open sources. Two most important data sources are the MAG data dump and Crossref.
Over the MAG migration, data changes certainly were introduced. It’s worth pointing out that OpenAlex introduced a lot of new data types that were not in MAG, such as Open Access (OA) status (powered via Unpaywall integration, also a free OurReseach tool), and unique and persistent identifiers for various entities, for example ISSN for journal titles, ORCID for authors, and ROR for institutions.
For a more detailed comparison of data format/features between OpenAlex and MAG (e.g., what’s gone, what’s retained), you may check out this page.
Access and Make Use of OpenAlex
OpenAlex is free and open source, and offer access via a web interface, API, and database snapshot.
API
The API is the primary way to query the OpenAlex dataset. The API output is in JSON format, which is easy to be read both by computers and humans.
For demonstration, let’s explore and search for some facts about HKUST’s research works. The results are better viewed at Firefox, as it has a built-in JSON viewer.
- Get general information about HKUST as an institution: https://api.openalex.org/institutions/ror:ror.org/00q4vv597
- Get counts of works by HKUST, grouped by publication year: https://api.openalex.org/works?filter=institutions.ror:https://ror.org/00q4vv597&group_by=publication_year
- Get counts of open access works by HKUST, grouped by publisher: https://api.openalex.org/works?filter=institutions.ror:https://ror.org/00q4vv597,is_oa:true&group_by=host_venue.publisher
Website – Coming Soon
The OpenAlex website (https://explore.openalex.org/), which is easier to use than API, is expected to be launched soon. For now, you can run some sample entity searches to get a taste of the design and interface. Let’s stay tuned for the official launch!
Database Snapshot
For most use cases, functions of OpenAlex API and the website explorer should be sufficient. However, one can also download and install a complete copy of the OpenAlex database on their own server and perform subsequent analysis. This page has instructions on how to download the snapshot and upload it to your own database.
You may follow OpenAlex on Twitter, and more documentation information is available at https://docs.openalex.org
– By Jennifer Gu, Library
Views: 2802
Go Back to page Top
- Category:
- Research Tools
published February 22, 2022


